by | BLOG, ECONOMY, TAXES
People have traditionally measured wealth by the amount of tangible assets they have. Viewed from this perspective, many people who have saved substantially for their retirement through an IRA, a 401K, or other profit sharing plans, (all in the category known as defined contribution plans) are well up in the highest percentile of people with wealth. Other people have retirement plans that provide only income streams for their (and often their spouse’s) lives. These are known as defined benefit pension plans. But since they do not have a pool of assets in a separately owned account, having rights only to the income stream – they are not viewed as having actual assets.
Therefore, these people are very often at the low end of the “asset” wealth scale. But the income stream is certainly an asset, a quite valuable one. And because of government policy and other economic factors in the last few years, the value of the defined benefit plans has exploded compared to the value of defined contribution plans. This has created a massive wealth switch to public service employees from private sector employees.
Given what the federal government’s policy has been with interest rates and fiscal policy, and given the much lower rate of return we have had to endure these last 6 years, the value of the retirement income stream has grown enormously, while the value of the retirement “nest egg” has diminished correspondingly. In this way, there has been a real conversion of income and assets such that people with continual income streams from defined benefit plans can now be looked at as having substantial “assets” while the retirement portfolio earning very little interest is less desirable. Being considered “wealthy” has become more about with having financial security than assets. The main reason for this switch can be found by examining the state of the pension system.
Say you have two people — one person in private industry, and one in the public sector, both making say $70K/year and hoping and expecting that they could retire on, say, $50K per year for all their years of good service and hard work.
It used to be, up until about 6 years ago, that a private industry person retiring with that $50K/year plan in mind could actually retire on that. The sum of his portfolio that would enable him to retire with that much per year would be around $1 million .That person could reasonably have concluded that he is set pretty well for life; if his portfolio earns 5% a year, he could pull out that $50k a year (5-% on a $1 million ) and still have the principal ($1 million ) left to pass on to the kids.
In a similar way, a public service worker or union making the roughly the same money would have roughly similar expectations — a $50K yearly pension. You could put a value on it ($1 million) but there is a large difference between the public pension and private pension. When the public pensioner dies, that pension ends; the money is gone. That is, there is no principal because there is no personal “investment portfolio” in the same manner that a private sector pensioner has. The public pension is funded from the larger investment pool within the public service industry.
Now, the last six years has made the pension and investment situation for retirees quite untenable. Interest rates remain sluggish, yielding only around 2% a year. That becomes only about $20K in returns for the private industry person. Now the pensioner can’t live off of the returns from the million in his portfolio. It’s not going to give him the retirement he planned or the inheritance he thought he could pass on. He needs more.
The situation is different for the public service person. He still gets his $50k a year, regardless of whether the return is actually 2% or 5%. His defined benefit plan promised to pay him a set amount every year until he passes away. When these plans were funded, and interest rates were a reliable 5%, the public service employers were only putting away enough to have $1 million worth per person, counting on yearly investment returns of 5%.
In order for the public service pension to get funded as promised , (at $50K/yr) the public service pension pool must pay it. Though the plan may have been “worth” a $1 million, now that the pool has to cough up the difference in funds due to low investment performance (2% in reality when 5% was necessary). That pension now becomes the valued at $2.5 million, ($2.5million x 2% = $50,000) because more funds are needed to supplement it in order to maintain the promised payments.
The government must come up with that extra $1.5 million supplement to sustain the promised benefits to the public service person. Multiply that by for every person for which there is not enough money set aside in these pooled retirement funds to pay for them. Where does that money come from? The employer? No, the taxpayer.
Here’s the kicker. When the public sector and unions earmarked that million for the employee, they hoped it would be enough to cover it. Within the private sector, over time business owners began to understand the fiscal instability and risk inherent in such defined benefit plans. Refusing to make such a commitment, most private sector employers have abandoned such plans completely.
When the public service sector started seeing the fissures in the system, they started to negotiate to keep their benefits as good as possible. But they didn’t, and still don’t, negotiate with the taxpayer. They negotiate with politicians, not the people who fund the retirement pool.
So what has really happened with these public and private retirement plans? Those public service persons with the $50K retirement plan saw the value of their retirement jump from $1 million to $2.5 million. From an accounting point of view, it’s money going into the assets of the public service employees, while the other side is a debt born to all the taxpayers for the benefit of a few.
This is nothing more than a huge wealth transfer. When the public sector and unions made deals with municipalities, these were cozy sweetheart deals, a trojan horse, a poison pill. There were no provisions made to handle the possibility of a low-interest rate society; they took their chances and their fallback was to suck money from the taxpayer by raising taxes to cover budgeting shortfalls.
Now the private sector pensioners are bearing the brunt on two fronts — their own retirement plans are performing poorly and their portfolios are dwindling while their taxes help to fund the gross negligence of the public sector. All taxpayers are feeling the pinch. The failure of the public service groups to be responsible in their fiduciary responsibility to the taxpayer means that now more than ever, vast amounts of wealth are being given over merely to band-aid this broken system, mask the true debt, and avoid real reform. This is politician/public service union cronyism for all to see.
by | ARTICLES, BLOG, ECONOMY, FREEDOM, OBAMA, POLITICS, TAX TIPS, TAXES
Forbes recently had a very good article which explores the US Federal Debt and how it affects economic growth. It also reviews government debt for the future, and its affect on the private sector and the debt-to-GDP ratio. Unfortunately, it doesn’t cover the entirety of US debt, which includes substantial entitlement obligations, but that’s probably fodder for another article entirely. If you want a decent primer on our federal debt — which translates into $154,161 each taxpayer owes towards it — read the article below.
The availability of credit in the U.S. was a major catalyst in the economic boom of the twentieth century. However, too much of a good thing can also be a problem. Is the U.S. too reliant on debt? Is the federal government mortgaging the future earnings of an entire generation? In this article, we’ll explore these and other issues as we take a look at the debt cycle in America.
The Impact of Debt on Economic Growth
In the early part of the twentieth century, if people didn’t have the money to purchase an item, they would save for it. With the introduction of credit terms, high-dollar items became much more affordable. It also changed the way we view debt. For example, rather than think of a new car in terms of its total price, we began to focus on the amount of the monthly payment. And, as the use of debt increased, the American standard of living rose with it. Excessive debt was also one of the primary catalysts for the economic boom of the 1980s, 1990s, and part of the 2000s. However, when debt is used in excess, it steals from the future since it must be repaid. This is because a dollar borrowed today necessitates that a dollar plus interest be repaid in the future. This reduces the amount of money available for future spending. If the amount of debt accumulated is significant and the period of accumulation is long, the required debt payments will negatively impact economic growth. What about government debt? How does it impact the future and the economy?
Government Debt and the Future
As I write this article, the federal government has accumulated $18.2 trillion of debt. In 2004, the federal debt was $7.3 trillion. This rose to $10 trillion when the housing bubble burst four years later. Today it exceeds $18 trillion and is projected to approach $21 trillion by 2019. When you break this down to an amount per taxpayer, the numbers are substantial. It has more than doubled over the past 11 years, rising from $72,051 per taxpayer in 2004 to $154,161 today. As the debt continues higher, the liability of every taxpayer is also rising. The change in the amount of the federal debt per taxpayer from 2004 to 2015 represents an average annual increase of 7.16%. This is much more than the average annual wage increase during the same period.
The Great Private Sector Extortion?
What problems might result from our fiscal failure? With the debt per taxpayer as high as it is, if the government continues to raise taxes on middle income earners and above, it will become increasingly difficult for many of these individuals to preserve their standard of living. This will result in a reduction of wealth that spans the entire income spectrum, excluding perhaps the super-rich. The difficulty will begin in the middle class and eventually creep toward the higher income earners if the debt problem persists. Why will this create difficulty? Because these individuals will be asked to pay higher taxes so the federal debt can be retired. It may be framed under a pretense of patriotism but will really be just another excuse to extract money from the private sector. As the private sector shrinks, economic activity will slow which will result in smaller wage increases. Therefore, these individuals will be squeezed from both ends (taxes and wages). This is one of the key reasons why the middle class is shrinking. It’s as if we’re all on the Titanic and people are continuing to sing and dance while the ship slowly sinks. Does the federal government have the ability to repay its debt? And, if it does today, what about in five or ten years? How difficult will it be then? Let’s address this question now.
The U.S. Debt-to-GDP Ratio
The debt-to GDP ratio compares the amount of the public debt to the size of the economy. For example, if GDP – which is the total of all goods and services produced in the U.S. – is $17.0 trillion and the debt is the same amount, the ratio would be 100%. As the debt rises beyond GDP, the ratio will exceed 100%. This indicates that the debt is greater than the total of what we produce. You might equate it to an individual’s debt-to-income ratio which helps lenders assess an individual’s ability to repay a loan. America’s debt-to-GDP ratio in 1980 was only 35.4%. Ten years later it was 57.7%. As you can see from the chart below, America’s debt-to-GDP ratio has continued to rise and today stands at 102.6%. Although this is not a staggering percentage, as an absolute number, $18.2 trillion in debt is very formidable.
Is the federal government getting in over its head? Will the mounting debt cause a financial hardship on Americans? As the debt continues to expand, the economy will continue to be sluggish, the tax burden will continue to grow, and the middle class will continue to shrink. If Washington doesn’t act soon, will the debt become an unmanageable burden? I believe the answer to this questions lies somewhere between “absolutely” and “very likely.” How bad could it get? It’s difficult to say. To change direction, however, we will need elected officials who are willing to put the needs of the country ahead of their own agenda. In other words, politics will have to take a back seat. You can be sure of this: You cannot circumvent the laws of economics. If we continue to accumulate debt, if we ignore the warning signs, if our officials maintain the status quo, there will be consequences. I only hope America realizes it before it’s too late.
by | ARTICLES, BLOG, FREEDOM, GOVERNMENT, OBAMA, POLITICS, TAXES
Each year, the Tax Foundation releases its annual report measuring Tax Freedom Day, “the day when the nation as a whole has earned enough money to pay its total tax bill for the year.” Tax Freedom Day is today. April 24th. It takes 114 days of working to pay the country’s tax bill.
Some important findings:
“Americans will pay $3.3 trillion in federal taxes and $1.5 trillion in state and local taxes, for a total bill of more than $4.8 trillion, or 31 percent of the nation’s income.
Tax Freedom Day is one day later than last year due mainly to the country’s continued steady economic growth, which is expected to boost tax revenue especially from the corporate, payroll, and individual income tax.
Americans will collectively spend more on taxes in 2015 than they will on food, clothing, and housing combined.
If you include annual federal borrowing, which represents future taxes owed, Tax Freedom Day would occur 14 days later on May 8.
Tax Freedom Day is a significant date for taxpayers and lawmakers because it represents how long Americans as a whole have to work in order to pay the nation’s tax burden.”
According to the Tax Foundation, the farthest Tax Freedom Day in the calendar year was in 2000, when Tax Freedom Day was May 1. That year, “Americans paid 33 percent of their total income in taxes that year. A century earlier, in 1900, Americans paid only 5.9 percent of their income in taxes, meaning Tax Freedom Day came on January 22. The last time Tax Freedom Day was this late in the year was 2007 (April 25).”
Additionally, Tax Freedom Day is calculated state-by-state. Some states have a more progressive tax system and higher taxes, and some have a lower tax burden. The latest Tax Freedom Day is found in New Jersey and Connecticut, whose Tax Freedom Days fall on May 13th. A few states have Tax Freedom Days earlier than the national Tax Freedom Day; Louisiana is the earliest on April 2nd. You can see how your state fares:
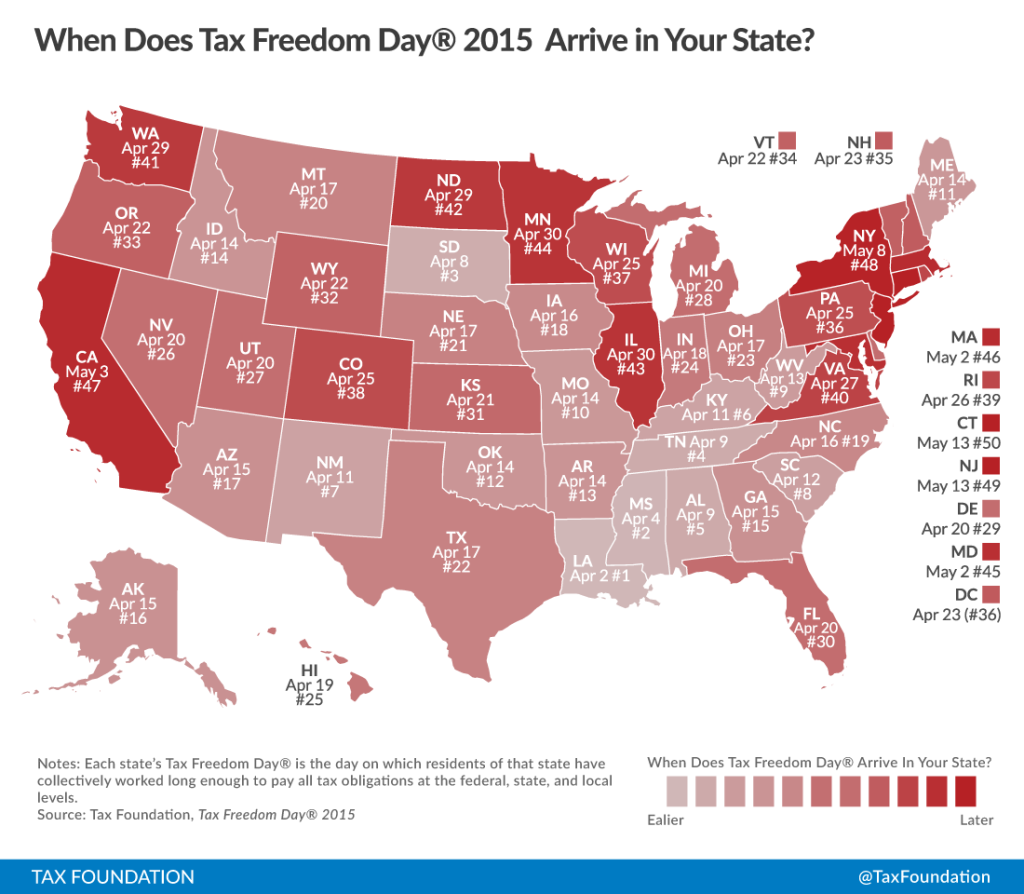
In case you are interested in the methodology of the Tax Foundation, they issues the following description: “In the denominator, we count every dollar that is officially part of national income according to the Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Economic Analysis. In the numerator, we count every payment to the government that is officially considered a tax. Taxes at all levels of government—federal, state, and local—are included in the calculation. In calculating Tax Freedom Day for each state, we look at taxes borne by residents of that state, whether paid to the federal government, their own state or local governments, or governments of other states. Where possible, we allocate tax burdens to the taxpayer’s state of residence. Leap days are excluded to allow comparison across years, and any fraction of a day is rounded up to the next calendar day.”
by | ARTICLES, BLOG, ELECTIONS, FREEDOM, OBAMA, POLITICS, TAXES
Earlier this year, John Koskinen, the IRS Commissioner, complained about the IRS budget given to him by Congress. It was reduced by nearly $350 million for this fiscal year. Commissioner Koskinen claimed the “agency’s $10.9 billion budget is its lowest since 2008. When adjusted for inflation, the budget hasn’t been this low since 1998.”
Due to budget cuts, the IRS warned that customer service would be reduced. The Taxpayer Advocate, (the IRS watchdog of sorts) recently gave her semi-annual report to Congress and discussed this issue at length. Among her findings were 1) if you call, it is likely that only half of the estimated 100 million people will ever reach an IRS agent on the other end; 2) hold times will exceed 30 minutes or more; and 3) the IRS is mandated to provide callers with the option to speak to a live person on its helplines, but would not even clarify to the Taxpayer Advocate which lines are designated helplines when calling in.
Now it seems that the dire, reduced customer service has already been happening for the past year and was orchestrated by the IRS itself. A new House Ways and Means report shows that, “while congressional funding for the IRS remained flat from 2014 to 2015, the IRS diverted $134 million away from customer service to other activities. In addition to the $11 billion appropriated by Congress, the IRS takes in more than $400 million in user fees and may allocate that money as it sees fit. In 2014, the IRS allocated $183 million in user fees to its customer service budget, but allocated just $49 million in 2015–a 76 percent cut.” How much more will they cut for FY2016? How much worse will customer service get?
Just as Obama dared to close national parks and monuments and cut off treatment for cancer kids during the government shutdown, in order to inflict pain on ordinary citizens, the IRS decided follow the same tactic and abrogate its basic responsibility to help taxpayers with compliance. Reducing the ability to provide customer service is particularly shameless.
For all the complaints about lack of budget funds, the Weekly Standard made note of a particular irony: “The IRS’s total annual $11 billion budget is dwarfed by the amount of improper tax payments it makes each year. According to the report, the IRS paid out $17.7 billion in improper Earned Income Tax Credit payments (which are supposed to help poor and low-income individuals) and an additional $6 to $7 billion in improper child tax credit payments.”
That’s double the amount of the entire IRS budget paid out to taxpayers incorrectly. Perhaps if the same amount of diligence the IRS took when targeting conservatives was paid to processing tax returns properly, there wouldn’t be such whining from the IRS Commissioner. And maybe some more phone calls would be answered.
by | BLOG, ELECTIONS, FREEDOM, OBAMA, POLITICS, TAXES
The vote to confirm Loretta Lynch might happen as early as this week. The process has been stretched out under the auspices of being contingent on passing a human trafficking bill in the Senate, but it is just as likely that the vote was put quietly on hold in a “logjam” until 51 votes were clinched for certain. It has been a struggle to get enough votes throughout the process, with the 51 vote only been secured at the beginning of April. 5 Senate Republicans that were needed are: Sens. Orrin Hatch (Utah), Lindsey Graham (S.C.) and Jeff Flake (Ariz.) — all members of the Judiciary Committee — and moderate Sens. Mark Kirk (Ill.) and Susan Collins (Maine).
Lynch’s opponents have been painted as racist and anti-immigrant. But the most abhorrent reason for nominating Lynch is truly in the realm of civil rights, with the media turning a blind eye to her antics, specifically related to civil asset forfeiture.
The most ironic about the matter is that “Ten civil and human rights organizations, including the National Action Network, which is headed by the Rev. Al Sharpton, the League of United Latin American Citizens and the NAACP wrote a letter to McConnell [last] Friday urging a vote on Lynch.
A couple of months ago, I wrote an open letter decrying the nomination of Loretta Lynch and spelled out her egregious record on the issue of civil rights, which should be chilling for anyone considering her nomination. I will repost it here below, since the media has failed to give any real scrutiny to her time in New York.
The nomination of Loretta Lynch to the position of Attorney General is before you. Although her intelligence, experience, and poise may appear to make her a superb candidate, it is clear now that she would be an extremely poor – even dangerous — choice due to her strong position on civil asset forfeiture.
The need to safeguard civil liberties and individual rights is a priority for all Americans. Do you really want to consider confirming a person who has been exceedingly proud of her record of taking property without due process…of practicing guilty until proven innocent? This is a very serious issue, not to be taken lightly.
Civil asset forfeiture is a particularly egregious abuse of power, allowing the government to seize property and cash if it merely suspects wrongdoing, even with no evidence and no charging of a crime.
Loretta Lynch was particularly lucrative in this regard as the U.S. attorney for the Eastern District of New York. Between 2011 and 2013, the forfeiture operations under her management netted more than $113 million in civil actions. Lynch’s division was among the top in the country for its collections. But this is not something to be proud of.
In one particularly appalling case, Loretta Lynch’s office seized nearly a half-million dollars from two businessman in 2012 and sat on it for more than two years without a court hearing or appearance before a judge. In fact, no crime had been committed. These men were denied due process and deprived of their assets without warning or criminal charges. Lynch suddenly returned the money just weeks ago on January 20, 2015 — on the eve of her confirmation hearings, having found no wrongdoing by the men either.
During Lynch’s confirmation hearing testimony pertaining to civil asset forfeiture, Lynch stated that “civil and criminal forfeiture are very important tools of the Department of Justice as well as our state and local counterparts.” She further argued that forfeiture is “ done pursuant to court order, and I believe the protections are there.” This is, in fact, not true. In the case mentioned above, there was not only no court order, but also no hearing at any time in nearly three years. That is unconscionable. And this is only one of many similar, well-documented, incidents.
The problem of civil asset forfeiture is that the government can confiscate money or property under the mere suspicion of a crime without ever actually charging someone. The person must prove his innocence to reclaim what was seized, which is a burden of time and money and readily seems to go against our staunch American belief of “innocent until proven guilty.” What’s more, besides the obvious threat to civil liberties, those most likely to be victims are poor and minority citizens.
Thankfully, in recent months, individuals and organizations on both sides of the political aisle have come together to demand reform to this unjust practice. Bipartisan legislation has been proposed in Congress; groups ranging from the Heritage Foundation to the American Civil Liberties Union have been increasingly critical of civil asset forfeiture practices. Even Eric Holder has called for changes and the IRS has recently and publicly pledged to reduce its involvement as well.
Loretta Lynch and her record on civil asset forfeiture represents the worst of this “tool for law enforcement”. A vote for her confirmation is a vote you will never be able to walk back. Do you really want to confirm a person who is so deeply committed to civil asset forfeiture at the very same time in America that there is strong bipartisan support for protecting civil liberties and walking back the laws pertaining to this practice? It makes no sense to proceed down this path.
Loretta Lynch may arguably be the most successful forfeiture agent in government today. This is not a positive quality for an Attorney General. The practice is abusive and her tactics even more so. Voting to confirm a person with such an atrocious civil liberties record is certain to cause problems for you down the road when you have to answer for your support. Therefore, on behalf of all Americans, I urge you to vote no for her confirmation.
by | ARTICLES, BLOG, BUSINESS, ECONOMY, GOVERNMENT, OBAMA, OBAMACARE, POLITICS, TAXES
I have no particular favorite right now in the GOP nomination fight. As a CPA, I pay close attention to the economic policies of the various candidates.
Carly Fiorina spoke to New Hampshire Republican Party’s First in the Nation leadership summit in Nashua, N.H on the subject of small business. Being the former CEO of Former Hewlett-Packard, Fiorina offered a decent perspective, which hasn’t really been discussed at length so far by many of the other candidates.
“The heroes of the American economy are small businesses and family-owned businesses”
“For the first time in U.S. history, we are destroying more businesses than we are creating”
“All of the things they are doing up there are landing on us down here. The weight of the government is literally crushing the potential of the people of this nation”
I don’t particularly think that Fiorina has the ability to be much of a viable candidate, especially considering her failed Senate campaign against Barbara Boxer in California. I do appreciate her calling out the government’s anti-business policies, something about which I have written extensively.
Whoever becomes the Republican nominee needs to be able to speak clearly and definitively about economic issues and call out the failed government policies of higher taxes, increased regulation, and minimum wage nonsense. Small businesses have borne the brunt of Obama’s heavy-handedness, and our economy has failed to recover adequately because of it.
by | ARTICLES, BLOG, ECONOMY, FREEDOM, OBAMA, POLITICS, TAXES
“Life, liberty, and property do not exist because men have made laws. On the contrary, it was the fact that life, liberty, and property existed beforehand that caused men to make laws in the first place” — Frédéric Bastiat in “The Law.”
If you haven’t read “The Law” yet, you can download it here for free. It is one of the most marvelous works of economics and philosophy.
by | ARTICLES, BLOG, FREEDOM, GOVERNMENT, OBAMA, TAX TIPS, TAXES
If you are an American living abroad — dubbed an “expat” — you are still expected to pay income taxes and file income tax reports to the IRS. The United States is the only country in the world that has this requirement and it is mandatory until and unless one renounces citizenship.
Being an expat in recent years has become more difficult. In 2010, Congress passed FATCA, which was enacted as a means to find foreign accounts of US taxpayers (such as a Swiss bank account). Overseas banks must also report to the IRS any bank accounts held by Americans; this has led to the unintended consequence of many banks choosing not to service expats because of the additional headache for the particular financial institution.
And now compliance has become even more onerous for expats. The IRS has announced the permanent closing its three remaining walk-in offices at the U.S. embassies in London, Paris, and Frankfurt, by the end of the fiscal year. Taxpayers abroad are expected to use the internet for all their tax needs. But woe to the international taxpayer who makes a filing mistake; you can be sure that the IRS will levy hefty fines.
Furthermore, even more simple transactions will be impacted by the office closings:
“For foreign citizens who need an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) to do things like sell property in the U.S. or claim dependents on a U.S. tax return, the process could be even more difficult. Ms. Otto, the accountant, says that when she was based in France, foreigners could get an ITIN by getting a notarized copy of their passport and submitting that with an ITIN application to the IRS at the embassy locations abroad.
But now foreigners who need an ITIN have to mail their passport to an IRS office in the U.S. for verification. “What person in his right mind is going to mail his passport to the IRS?” she asks.”
The number of taxpayers living abroad has grown substantially in the last five years, with some estimates as much as a 50% increase. It is certainly not a time to reduce services to our overseas Americans. However, the IRS sees fit to protest budget cuts by doing that — just not just abroad, but in all facets of customer service to taxpayers.
*To get an idea of tax compliance for expats, check out this very good, comprehensive list of important forms below
Common Overseas Tax Forms
Form 2555 & 2555- EZ: These forms are for calculating your Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) and to calculate your Foreign Housing Exclusion or Deduction. If you meet certain foreign residency requirements, you may be able to exclude up to $99,200 of earned income in 2014 and a portion of your foreign housing expenses from U.S. income tax. Note that this exclusion does not apply to self-employment taxes. If you are self-employed abroad, you are still subject to U.S. Social Security taxes unless you live in one of the 25 countries with which the U.S. has a Social Security Totalization Agreement. The FEIE is generally advantageous to use when income tax rates in the foreign country are lower than in the U.S. and/or your total earned income is below the exclusion threshold.
Form 1116: This is the Foreign Tax Credit form and it is used to claim a credit against your U.S. income tax for income taxes paid in the foreign country. This credit applies both to foreign earned income (wages, self-employment income, etc.) and unearned income (interest, dividends, capital gains, rents, etc.). This is generally the most beneficial form to use for residents of countries with high income tax rates, those with children eligible for the additional child tax credit and those interested in contributing to U.S. retirement plans (traditional and Roth IRAs, SEPs, solo 401(k)s, etc.)
FBAR Form FinCEN 114: This form is independent of the tax return and a separate filing requirement. The FBAR applies to any U.S. person who owns, has beneficial interest or signature authority over foreign financial accounts that exceed $10,000 in the aggregate in value at any time during the year. If you have any foreign bank accounts, this also has to be disclosed on Part III of Schedule B, whether the FBAR is required to be filed or not. FinCEN 114 must be e-filed and cannot be mailed, with the absolute filing deadline on June 30, with no extension possible.
Form 8938: This form, also known as the Fatca form, is used to report Specified Foreign Financial Assets and the income derived from them. There is some overlap with the FinCEN 114 Form (FBAR), but the filing thresholds are higher, and depend on the taxpayer’s residency and marriage status, with different thresholds for the highest value reached during the year and on the last day of the year. These thresholds range from a low of $50,000 to a high of $600,000.
Other Overseas Tax Forms
Not every tax preparer will be familiar with the forms described below. If any of these forms apply to your situation, you will need to make sure that your preparer is qualified to do the work. Many of these forms are quite complex and require special training to prepare. The IRS, for example, estimates that each Form 8621 requires almost 17 hours of record-keeping and more than 14 hours to prepare. These are the forms that are most commonly missed or filed with errors. The list that follows is illustrative and not comprehensive:
If you received a gift or inheritance from a foreign person, even though it will generally not be taxable in the U.S., depending on the amount, you may have to report it in Form 3520. This form is also used to report transactions that you had with foreign trusts. If you are grantor in a foreign trust, you are likely required to file Form 3520-A in addition to form 3520.
If you run your own business in a foreign country, you may have established a company to conduct your business. Depending on the entity’s classification for U.S. tax purposes, which will be a corporation by default or will depend on the classification election made through Form 8832, you may be required to file Form 8858 if the entity is disregarded; Form 5471 if the entity is classified as a corporation; or Form 8865 if classified as a partnership. Transactions between you and your foreign company may have to be reported on Form 926.
If you live in a country with which the U.S. has an income tax convention, you may be entitled to certain treaty benefits with respect to your foreign retirement accounts, re-sourcing of certain U.S. source income to avoid double taxation, taxation of foreign social security, etc. The treaty-based positions taken in your return may have to be disclosed in Form 8833.
If you have a brokerage account or other investments (including some foreign retirement accounts) in a foreign country, these investments may be classified as Passive Foreign Investment Companies or PFICs, which are subject to special tax rules that are generally unfavorable in nature. Most foreign mutual funds and ETFs are classified as PFICS. Each PFIC you own is reported on a separate Form 8621.
Other forms that could also apply to your situation include Form 5173: Transfer Certificate which is issued by the IRS upon the death of an American citizen overseas, and is a discharge form confirming that all taxes had been paid and which is often required by banks and brokerage firms to release funds to the estate; Form 5472 for certain U.S. corporations with 25% foreign ownership and certain foreign corporations engaged in a U.S. trade or business; and Form 720, Quarterly Excise Tax Return, to report and pay excise taxes on certain foreign life insurance premiums.
Common Tax Forms – With Some Overseas Components
The following forms are common for U.S. taxpayers but also have some international elements to be aware of:
1040: Ultimately all of your income (foreign and domestic) should end up on your form 1040. Americans married to non-Americans may be able to us the Head of Household filing status instead of married filing separately. In some cases adding a non-citizen spouse (and their income and assets) to the U.S. tax return can be beneficial. All dependents on the return, must have a U.S. tax ID number.
1040: – Schedule A: Some expenses related to being overseas may be able to be claimed as itemized expenses such as certain foreign taxes, certain moving expenses and travel, mortgage interest, medical and dental expenses etc.
1040: – Schedule B: Part III of Schedule B has information related to foreign trusts and foreign bank accounts. Make sure you check these correctly.
1040: – Schedule C. If you live overseas and are self-employed, you will still have to file a Schedule C. You may be subject to U.S. Social Security though Totalization Agreements may negate the need for paying into U.S. Social Security. You will also generally be able to contribute to a U.S. solo 401(k) or SEP IRA but these may not be tax-deferred in the country where you live and work.
For more information about overseas tax returns, you should check the IRS’s website, which has thousands of pages for your reading pleasure in a section dedicated to International Taxpayers. A good starting point for any new overseas American is Publication 54: Tax Guide for US Citizens and Resident Aliens Abroad.
