by | ARTICLES, BLOG, BUSINESS, ECONOMY, FREEDOM, GOVERNMENT, OBAMA, OBAMACARE, POLITICS, TAXES
The Hill has an interesting article about Obamacare, premium costs, and insurance companies. Insurers have been losing money as a result of the Obamacare set-up, and many are facing increased financial security. From the article:
Insurers say they are losing money on their ObamaCare plans at a rapid rate, and some have begun to talk about dropping out of the marketplaces altogether.
“Something has to give,” said Larry Levitt, an expert on the health law at the Kaiser Family Foundation. “Either insurers will drop out or insurers will raise premiums.”
While analysts expect the market to stabilize once premiums rise and more young, healthy people sign up, some observers have not ruled out the possibility of a collapse of the market, known in insurance parlance as a “death spiral.”
In the short term, there is a growing likelihood that insurers will push for substantial premium increases, creating a political problem for Democrats in an election year.
Insurers have been pounding the drum about problems with ObamaCare pricing.
The Blue Cross Blue Shield Association released a widely publicized report last month that said new enrollees under ObamaCare had 22 percent higher medical costs than people who received coverage from employers.
A report from McKinsey & Company found that in the individual market, which includes the ObamaCare marketplaces, insurers lost money in 41 states in 2014, and were only profitable in 9 states.
“We continue to have serious concerns about the sustainability of the public exchanges,” Mark Bertolini, the CEO of Aetna, said in February.
The Aetna CEO noted concerns about the “risk pool,” which refers to the balance of healthy and sick enrollees in a plan. The makeup of the ObamaCare risk pools has been sicker and costlier than insurers hoped.
The clearest remedy for the losses is for insurers to raise premiums, perhaps by large amounts — something Republicans have long warned would happen under the healthcare law, known as the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
“The industry is clearly setting the stage for bigger premium increases in 2017,” said Levitt of the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Insurers will begin filing their proposed premium increases for 2017 soon. State regulators will review those proposals, and then can either accept or reject them.
Michael Taggart, a consultant with S&P Dow Jones Indices, pointed to data from his firm showing per capita costs for insurers are spiking in the ObamaCare marketplaces.
“We made a significant change in the rules with the ACA and we’re still working through the process to see how that market stabilizes,” Taggart said at a panel on Wednesday. “Is [a death spiral] a possibility? Sure it’s a possibility. I wouldn’t attempt to put a probability on it because I think there are a lot of things going on.”
One factor helping to prevent a death spiral is ObamaCare’s tax credits, which cushion the impact of premium increases on consumers.
“What we’re likely to see is more of a market correction than any kind of death spiral,” Levitt said. “There are enough people enrolled at this point that the market is sustainable. The premiums were just too low.”
Dr. Mandy Cohen, the chief operating officer of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), said in an interview that there is “absolutely not” a risk of a death spiral or collapse in the ObamaCare marketplaces.
While acknowledging that “companies are needing to adjust” to the new system, she pointed to the 12.7 million people who signed up this year, 5 million of whom were new customers, as a sign of success.
“What brings us the most confidence about the long term stability and health of the marketplace is its growth,” Cohen said.
Another risk, should regulators reject large premium increases, is that insurers could simply decide to cut their losses and drop off the exchanges altogether.
“Given that most carriers have experienced losses in the exchanges, often large losses, it only makes sense that most exchange insurers will request significant rate increases for 2017,” said Michael Adelberg, a former CMS official under President Obama and now a consultant at FaegreBD.
“Market exits are not out of the question if an insurer is looking at consecutive years of losses and regulators are unable to approve rates that get the insurer to break-even.”
The most prominent insurer eyeing the exits is UnitedHealth, which made waves in November by saying it was considering whether to leave ObamaCare in 2017 because of financial losses. The company last week announced that it is dropping its ObamaCare plans in Arkansas and Georgia, and more states could follow.
The Department of Health and Human Services argues that the attention on UnitedHealth is overblown, given that the insurer is actually a fairly small player in the marketplaces.
It’s more important to watch what happens with Blue Cross Blue Shield plans, which are the backbone of the ObamaCare marketplaces.
There have been some rumblings of discontent from Blue Cross plans. The plan in New Mexico already dropped off the marketplace there last year after it lost money and state regulators rejected a proposed 51.6 percent premium increase. Now, Blue Cross Blue Shield of North Carolina says that it might drop out of the marketplace because of its losses.
Blue Cross of North Carolina CEO Brad Wilson said in an interview that the company had lost $400 million due to its ObamaCare business.
“We’re not alone and I think that that also is evidence to suggest that there are systemic and fundamental challenges that we all need to have a civilized conversation about,” Wilson said.
He said a key factor in the decision on whether to stay in the market next year will be whether regulators approve whatever premium increase the company ends up proposing so as to try to make up for its losses.
Asked about the risk of a death spiral, Wilson said he is not worried about that happening “tomorrow,” but has concerns if the situation does not change over time.
“There’s not going to be something magical happen that will cause this to turn around,” Wilson said. He is pressing for changes like further tightening up extra sign up periods that insurers say people use to game the system, and repealing the Health Insurance Tax, which could help lower premiums.
Dr. Cohen of CMS said that her agency is in close touch with insurers and Blue Cross Blue Shield of North Carolina in particular. But she pushed back on talk of Blue Cross of North Carolina dropping out of the marketplace, stating flatly that, “I have no concerns about them leaving the market.”
She referred to problems the company has had with its computer systems that have led to some people being enrolled in the wrong plan, along with other issues that have added to the company’s administrative costs.
by | ARTICLES, BLOG, BUSINESS, ECONOMY, FREEDOM, GOVERNMENT, OBAMA, POLITICS, TAXES
A short but informative article by the Washington Free Beacon describes how the Government Accountability Office (GAO) has calculated that within a few years, the federal government will owe more money that the sum of what is produced by the economy. That, my friends, is an egregious amount of debt.
“Gene Dodaro, the comptroller general for the Government Accountability Office, testified at the Senate Budget Committee to provide the results of its audit on the government’s financial books.
“We’re very heavily leveraged in debt,” Dodaro said. “The historical average post-World War II of how much debt we held as a percent of gross domestic product was 43 percent on average; right now we’re at 74 percent.”
Dodaro says that under current law, debt held by the public will hit a historic high.
“The highest in the United States government’s history of debt held by the public as a percent of gross domestic product was 1946, right after World War II,” he said. “We’re on mark to hit that in the next 15 to 25 years.”
Another economic projection which assumes that cost controls for Medicare don’t hold and that healthcare costs continue to increase, shows debt rising even further.
“These projections go to 200, 300 percent, and even higher of debt held by the public as a percent of gross domestic product,” said Dodaro. “We’re going to owe more than our entire economy is producing and by definition this is not sustainable.”
Additionally, the audit found fault with the number of improper payments that should not have been made or were the incorrect amount. The audit found that in fiscal year 2015 there were $136.7 billion improper payments, which was up by $12 billion from the year prior.
The audit also called into question the reliability of the government’s financial statements. According to the report, if a federal entity purchases a good or service, that cost should match the revenue recorded by the federal entity that sold the good or service. The report found that this was not always the case and found hundreds of billions of dollars in differences between transactions between federal entities.
“The government-wide financial statements that the GAO audits tell us what came into the government’s coffers and what went out, what the government owns and what it owes, and if the operations are financially sustainable,” said Sen. Mike Enzi (R., Wyo.). “But can we trust the information in the statements?”
“GAO’s audit calls into question the reliability of the underlying financial data,” he said. “The sketchiness is such that GAO remains unable to even issue an audit opinion on the government’s books.”
According to the audit, these weaknesses will eventually harm the government’s ability to reliably report their assets, liabilities, and costs, and this will prevent the government from having the information to operate in an efficient and effective manner.
by | ARTICLES, BLOG, BUSINESS, ECONOMY, FREEDOM, GOVERNMENT, OBAMA, POLITICS, RETIREMENT, TAXES
The Financial Times reviewed data recently that suggested that the US public pension system is in dire straits; the funding shortage is likely 3 times as large as what is being reported. The estimated deficit is $3.4 trillion.
The solutions for the funding shortfalls are grim: either raise taxes or cut spending; unfortunately the “cut spending” approach always goes to the essential services first, so that taxpayers feel the heat and will consider a tax hike instead.
US Congressman Devin Nunes recently noted that, “It has been clear for years that many cities and states are critically underfunding their pension programmes and hiding the fiscal holes with accounting tricks.” Nunes has “put forward a bill to the House of Representatives last month to overhaul how public pension plans report their figures.” He added: “When these pension funds go insolvent, they will create problems so disastrous that the fund officials assume the federal government will have to bail them out.”
Insolvency has already been observed in San Bernardino, California and Detroit, Michigan, largely due to mismanagement of pension funding and budget shortfalls. The Financial Times noted that “Chicago, Dallas, Houston and El Paso have the largest pension holes compared with their own revenues”, as well as the states of Illinois, Arizona, Ohio, and Nevada.
Research done by Stanford paints a difficult future: “Currently, states and local governments contribute 7.3 per cent of revenues to public pension plans, but this would need to increase to an average of 17.5 per cent of revenues to stop any further rises in the funding gap.”
And more: “Several cities and states, including California, Illinois, New Jersey, Chicago and Austin, would need to put at least 20 per cent of their revenues into their pension plans to prevent a rise in their deficits, while Nevada would have to contribute almost 40 per cent.”
Much of the problem lies in the fact that retirement costs and liabilities have consistently been calculated on a 7%-8% return , which is not particularly realistic, as has been demonstrated in recent years during the economic downturn.
There is no way this silent funding crisis will get any better — and until localities recognize and admit their crisis and make ardent changes to their pension systems, it will only continue to worsen egregiously.
by | ARTICLES, BUSINESS, ECONOMY, FREEDOM, GOVERNMENT, OBAMA, POLITICS, TAX TIPS, TAXES
The Fix the Debt Campaign Steering Committee is a bipartisan group of prominent leaders and experts, including luminaries such as Erskine Bowles and Alan Simpson, the co-chairs of the White House Fiscal Commission. The Fix the Debt group put together some decent graphics regarding federal spending.
This is a “taxpayer receipt” highlighting where the money goes and highlight where it comes from in the first place.
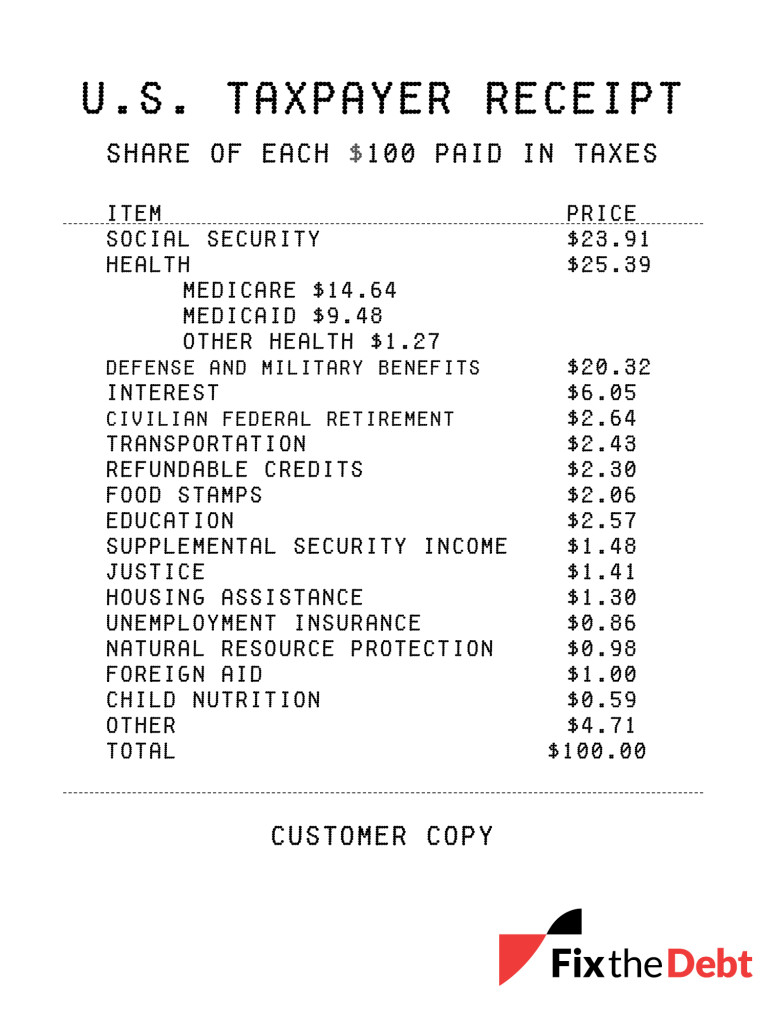
How are our federal tax dollars spent? As the taxpayer receipt illustrates, more than $75 of every $100 paid in federal taxes goes to Social Security, federal health care, defense, and interest on the debt. And the amounts for Social Security, health care, and interest are forecast to grow considerably in the years to come.
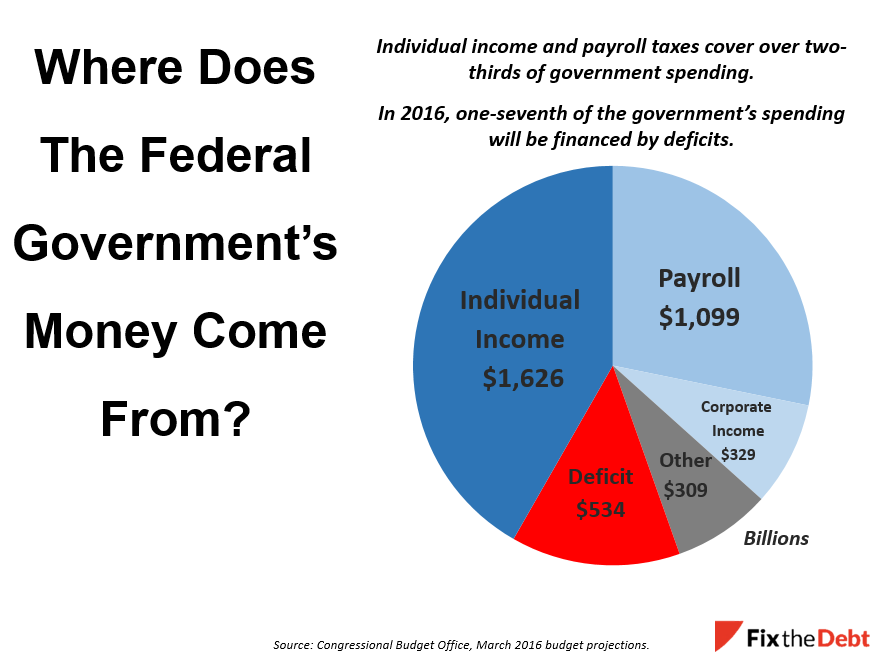
Where does the money come from? Much of the revenue for the federal government comes from the individual income tax that many of us are rushing to complete. Another major source is the payroll tax, which is the “FICA” tax that is withheld from your paycheck. It is used to fund Social Security benefits and parts of Medicare.
But a significant part of the government is deficit financed because spending exceeds revenue. That share is expected to grow substantially in the years ahead.
Check out their blog for more information.
by | ARTICLES, BUSINESS, ECONOMY, FREEDOM, GOVERNMENT, HYPOCRISY, POLITICS, TAXES
Yesterday, The Treasury Department made more changes to rules with regard to inversions. The driving force behind the constant meddling into this legal practice is the retention of tax revenue.
“Under the new rules, there will be a three-year limit on foreign companies bulking up on U.S. assets to avoid ownership requirements for a later inversions deal, Treasury said in a statement.”
In an inversion, a U.S. company typically buys a smaller foreign rival and reincorporates to the rival’s home country, which moves the company’s tax domicile, though core management usually stays in the United States.
The Treasury, which had last introduced new rules in November to curb inversions, also is proposing tackling the practice of post-inversion earnings stripping with new limits on related-party debt for U.S. subsidiaries.”
This continued attack on inversions is ridiculous and companies are being targeted unfairly because they represent a possible loss of revenue for the government. Inversions are legal, and sometimes necessary. They are a way for U.S. companies to change their HQ from the U.S. to a foreign country, for the sole purpose of allowing themselves the express privilege of being on par with foreign companies and eliminate the severe disadvantage that the U.S. puts on its own businesses via excessive taxes!
It is outrageous that the government applies such discrimination. It is outrageous that American companies have to chose to move their headquarters elsewhere simply to survive and compete globally, because they are taxed on their profits in two jurisdictions — both domestic and foreign.
by | ARTICLES, BLOG, ECONOMY, ELECTIONS, FREEDOM, GOVERNMENT, OBAMA, OBAMACARE, POLITICS, TAXES
Everything we were promised with Obamacare has yet to come to fruition: keep your plan! lower prices! tens of millions insured! and a litany of other broken promises and predictions.
Obamacare was signed into law on March 23, 2010. The Weekly Standard took the time to perform a thorough examination on the current state of Obamacare, an audit perhaps, comparing what was promised and what has been delivered. Their findings are sobering. It also offers some remedies of the most egregious maladies plaguing this particular legislation. I have reprinted the article in its entirety below, because it is chock-full of good information:
Three years ago, on the eve of Obamacare’s implementation, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) projected that President Obama’s centerpiece legislation would result in an average of 201 million people having private health insurance in any given month of 2016. Now that 2016 is here, the CBO says that just 177 million people, on average, will have private health insurance in any given month of this year—a shortfall of 24 million people.
Indeed, based on the CBO’s own numbers, it seems possible that Obamacare has actually reduced the number of people with private health insurance. In 2013, the CBO projected that, without Obamacare, 186 million people would be covered by private health insurance in 2016—160 million on employer-based plans, 26 million on individually purchased plans. The CBO now says that, with Obamacare, 177 million people will be covered by private health insurance in 2016—155 million on employer-based plans, 12 million on plans bought through Obamacare’s government-run exchanges, and 9 million on other individually purchased plans (plus a rounding error of 1 million).
In other words, it would appear that a net 9 million people have lost their private health plans, thanks to Obamacare—with a net 5 million people having lost employer-based plans and a net 4 million people having lost individually purchased plans.
None of this is to say that fewer people have “coverage” under Obamacare—it’s just not private coverage. In 2013, the CBO projected that 34 million people would be on Medicaid or CHIP (the Children’s Health Insurance Program) in 2016. The CBO now says that 68 million people will be on Medicaid or CHIP in 2016—double its earlier estimate. It turns out that Obamacare is pretty much a giant Medicaid expansion.
To be clear, the CBO—which has very generously labeled Obamacare’s direct subsidies to insurance companies as “tax credits,” even though sending money to insurers doesn’t lower anyone’s taxes—isn’t openly declaring that Obamacare has reduced the number of people with private health insurance or that it has doubled the number of people on Medicaid or CHIP. Rather, the CBO maintains that Obamacare has actually increased the number of people with private health insurance by 9 million and has increased the number of people on Medicaid or CHIP by (just) 13 million. But it would seem that the only reason the CBO can make these claims is that it has moved the goalposts.
That is, the CBO has significantly altered its estimates for what 2016 would have looked like if Obamacare had never been passed. In 2013, the CBO projected that, in the absence of Obamacare, 186 million people would have had private health insurance in 2016, and 34 million people would have been on Medicaid or CHIP. The CBO now maintains that, in the absence of Obamacare, only 168 million people would have had private health insurance in 2016 (a reduction of 18 million people from its 2013 projection), while 55 million people would have been on Medicaid or CHIP (an increase of 21 million people from its 2013 projection). Somehow the hypothetical non-Obamacare world has changed a lot in the past three years. (The CBO doesn’t explain how this could have happened.)
Even the CBO’s revised figures for a non-Obamacare world, however, can’t gloss over the fact that Obamacare has failed to hit its target for private health insurance by 24 million people. To see that, one must simply compare Obamacare’s new tally of 177 million to its 2013 target of 201 million.
The CBO doesn’t release retroactive scoring of Obamacare. Try finding, for example, tallies from the federal government (whether from the CBO or otherwise) on what Obamacare has actually cost so far. Rather, the CBO is like a handicapper who predicts the results of horseraces, but then never bothers to publish the races’ actual results.
Now that it’s clear enough, however, that Obamacare is basically an expensive Medicaid expansion coupled with 2,400 pages of liberty-sapping mandates, it’s time for a winning Obamacare alternativeto emerge, one along the lines of what Ed Gillespie almost rode to victory in the Virginia Senate race. Such an alternative should address the longstanding inequity in the tax code—between employer-based and individually purchased insurance—while adhering to four basic notions:
1. It shouldn’t touch the tax treatment of the typical American’s employer-based plan.
2. It should close the tax loophole on the employer side—which says that the more you spend (on insurance), the more you save (in taxes)—by capping the tax exclusion at $20,000 for a family plan (while letting anyone with a more expensive plan still get the full tax break on that first $20,000).
3. It should offer a simple tax break for individually purchased insurance that isn’t income-tested and thus doesn’t pick winners and losers (in marked contrast with Obamacare, which is all about picking winners and losers.)
4. It shouldn’t provide direct subsidies to insurance companies like Obamacare does. (The federal government provides a tax break for mortgage interest paid—it doesn’t directly pay a portion of people’s mortgage bills. Likewise, it shouldn’t directly pay people’s health insurance bills as if it were some kind of “single payer.”)
In addition, anyone crafting an Obamacare alternative should keep this important point in mind and express it publicly: Far from being the gospel truth, the CBO’s scoring is more like a wild guess that will never be checked against future reality.
by | ARTICLES, BUSINESS, ECONOMY, FREEDOM, GOVERNMENT, POLITICS, TAXES
Dustin Howard over at Americans for Limited Government tackles one of the key factors contributing to the rise of corporate inversions: high corporate taxes. I would also argue that another mitigating factor is foreign-earned income, which the United States government lays claim to — and is the only major country to do so. Under U.S. tax law, U.S. companies are forced to pay both foreign- and domestic-earned income, putting them at a global disadvantage.
At any rate, Howard’s piece is a worthwhile read on the equally detrimental effect of high corporate tax rates. I have shared it in its entirety below.
“How should policymakers stop the bleeding of American jobs overseas? There’s one easy answer among many harder ones, and that is to stop making it so expensive to do business in the United States.
Many things price American workers out of competition, whether it be the current mix of trade rules, currency manipulation and other unfair labor practices but the easiest to address domestically is the corporate tax rate. Government’s unwillingness to do with less is making it considerably harder for Americans to even work.
Seriously, why should American corporations pay a 39 percent rate, among the world’s highest, to headquarter here when they can “invert” to Ireland and pay 12.5 percent, less than one third the domestic rate?
If the corporation can keep most of their American workforce and keep 26.5 percent more of their money as an alternative by cutting the corporate tax rate, wouldn’t that a good thing?
Why would the U.S. maintain a policy that discourages business from even being on American soil?
Democrats propose a solution to this phenomenon: punish the innovating refugees that refuse to pay into their racket. They believe in taxing the profits of inverted firms. One problem: extrapolating from a recent study by economist Wayne Winegarden for the Pacific Research Institute, this actually further discourages firms from even retaining their American workforce, and encourages them to simply export their products outright from their new foreign addresses.
Call it a lose-lose proposition, where American workers lose jobs, American businesses leave and revenues drop while the deficit increases; Ireland should chip in and send Democrats a fruit basket.
If taxing inverted companies suddenly sounds unappealing, here’s an alternative: make inversions less attractive as a means of generating profit. The U.S. is a free country, so it looks bad when it punishes corporations for acting in their best interest. Instead, why not lower the tax rate to a more competitive, attractive rate, and then focus rolling back the regulatory state that is literally paid by taxpayers to make businesses less productive?
The first step on this path would be to begin reducing the cost of business with a comprehensive set of tax reforms that clean up our messy corporate tax code, and give businesses a sense of calm when planning for the future.
Besides it’s not like the corporate tax generates that much revenue anyway, at just 10.6 percent of $3.2 trillion of total receipts in 2015, according to the Office of Management and Budget. By far the most revenue comes from individual and payroll taxes.
As things stand, corporations are seeking foreign shores to chart out profitable futures, mainly because the business climate in the U.S. has made itself so volatile that it cannot accomplish that at home. The data supports the notion that punishing corporations that choose foreign domiciles will hurt working Americans more than it will avenge or protect them. The limited government solution is to let individuals choose what works for them, and to tax them at a reasonable rate so they do not move out of necessity.
As stated above, lowering the corporate tax rate is just one part of the solution. America has fundamental problems across the board that put us at a global disadvantage that should also be addressed.
The corporate tax rate is a necessary first step to signal to the world that we are restructuring the policies to make the U.S. more attractive among competitors. Creating jobs in America begins with keeping the economy free and competitive, and that cannot happen without fiscal restraint and limiting government, but also cannot happen if we’re taxing ourselves to the stone age.
by | ARTICLES, BLOG, ECONOMY, FREEDOM, GOVERNMENT, POLITICS, TAXES
The following is a short version of a recent talk by Ben Eisen regarding the minimum wage issue as a poverty-fighting tool. It is undeniable that the percentage of full-time workers in poverty is much less than part-time workers. “He explained – using sound economic theory and admirable coverage of empirical findings – that the minimum wage is as effective a tool for fighting poverty as is gasoline as a tool for fighting fires.
One of the stats that Ben cited is that only three percent of workers who work full-time year ’round live below the poverty line, while sixteen percent of workers who work only part-time live below the poverty line. (I can’t recall if Ben’s stats are for Canada or the U.S., but because the general trend no doubt holds in nearly all countries, whether Ben’s specific stats are for Canada or the U.S. doesn’t matter for purposes of my post here.)
Here’s a mental experiment (one that I might have offered, in some form, in the past): suppose that Pres. Hillary Clinton or Pres. Bernie Sanders – displaying to the public her or his courageous opposition to poverty – cites the stat that Ben mentioned and then proposes that government outlaw part-time work. “Because every worker should be able to live decently upon his or her earnings,” proclaims the president, “and because working full-time enables a worker to earn more income than that worker earns when working only part-time, it shall hereby be the law of the land that every worker must be employed full-time.”
I’m pretty sure even the most ardent supporter of the minimum wage would balk at such a proposal. But why? What’s the difference between minimum-hour legislation and minimum-wage legislation? If government dictates that each worker shall be paid no less than $X per hour, and if this diktat has no effect on workers other than ensuring that no worker is paid less than $X per hour, what reason is there to suppose that if government dictates that all jobs shall be full-time jobs that this diktat have any effect on workers other than ensuring that all workers will now be employed full-time – and, hence, that the number of people living in poverty will fall?
Put differently, if government can work miracles when it dictates hourly wages, why can’t it work miracles when it dictates hours of work?”
by | ARTICLES, BLOG, ECONOMY, FREEDOM, GOVERNMENT, OBAMA, POLITICS, TAXES
According to an economist at the Congressional Budget Office (CBO), the federal government should examine the question of taxing drivers by the mile as a means of raising higher revenue for highway programs.
According to the Washington Examiner, “Chad Shirley, CBO’s deputy assistant director for microeconomic studies, gave a presentation that says federal gas tax revenues are falling short of federal spending on highway programs. But to resolve that problem, Shirley didn’t propose less federal spending, and instead offered three suggestions.”
1) Charge drivers more through the implementation of a “vehicle-miles traveled charges.”
2) Charging them more when traffic is bad. Shirley calls that “congestion pricing.”
3) Charging tolls on “additional existing interstates.”
The idea of a “vehicle miles traveled tax,” or a “VMT” tax, was considered in 2011 in a bill that never came to fruition. That plan “foresaw the installation of equipment on people’s cars and trucks that would measure how far they drive, and the collection of taxes electronically through a reading of those devices at gas stations.”
Whether or not these new suggestions will be considered again remains to be seen. The CBO says that its three suggestions are not higher taxes or fees, but as an attempt to “make federal highway spending more productive for the economy.”
Such proposals are invasive of people’s privacy, and represent another ridiculous attempt at trying to regulate the behaviors of people.
by | ARTICLES, BLOG, ECONOMY, FREEDOM, GOVERNMENT, POLITICS, TAXES
The great Don Boudreaux a friend of mine, made mention of this picture last week over on his superb blog, Cafe Hayek. The picture is apparently a favorite among Trump supporters.

“What to say? Perry Potts Eidelbus, a Facebook friend, describes it as “a distillation of economic ignorance into pure form.” Indeed. It’s much like Trump himself: the very image of economic ignorance.
Trump is doing now from the political right what Paul Krugman has done so successfully over the past decade and a half from the political left, which is the following: boisterously assuring people that their untutored instincts about the economy are indeed accurate – telling people that what they immediately see in economic affairs and policies is all that there is to see in economic affairs and policies (that is, that there is no ‘unseen’ whose reality can be perceived and understood only by looking beyond that which is immediately obvious). According to this bastardized, pandering version of economics, actual consumable goods (such as are pictured here) are reckoned to be costs, while toil is reckoned to be a benefit. The economic problem is not rooted in scarcity, it is rooted in abundance. Social benefactors, therefore, are those who promise to deny to us the fruits of the economy’s abundance (along with, by the way, our economic freedoms) as they bestow upon us ever-greater scarcity that will bless us with the need for more toil.
The photo shown here is, in short, itself an intellectual cargo ship loaded down with countless tons of economic ignorance.”


